Introduction of Fake News Challenge
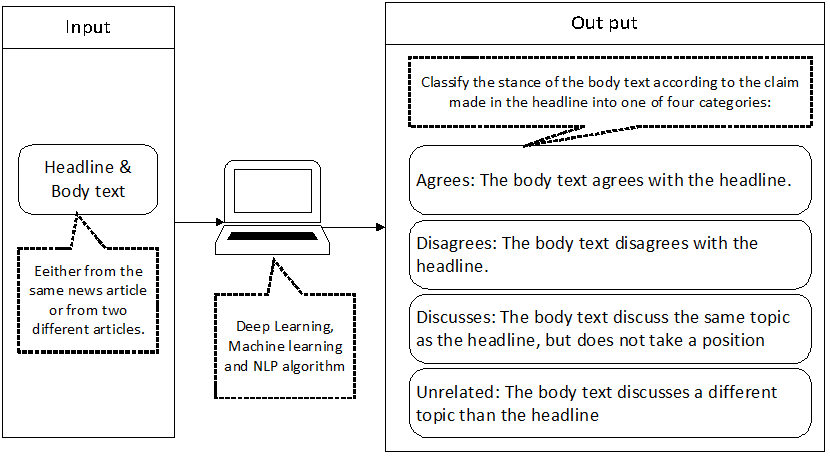
Fake news has been a topic covered significantly by media ever since the 2016 United States presidential election. In an in-depth paper, Facebook defines fake news as articles that purport to be factual, but contain intentional mis-statements of fact with the intention to arouse passions, attract viewership, or deceive. New Media Companies like Facebook and Twitter enable news stories and rumours to be propagated fast globally without proper verification procedures. It is important that strategies for identifying fake news and mitigating its spread could be developed. The Fake News Challenge (FNC-1) was organized under this background which aims to explore how Artificial Intelligence technologies, partially deep learning and natural language processing, might be leveraged to combat the fake news problem. In 2017, the competition phase one launched which focuses on the task of Stance Detection. Stance Detection can be regarded as the automating process of looking at what other news organizations are saying about a given claim, which is an important component for fake news detection. This process involves estimating the relative perspective (or stance) of two pieces of text relative to a topic, claim or issue.
Objective of this Project
The Objective is to develop an innovative stance detection algorithm by learning from the algorithms of the top three FNC-1 teams. It is expected that the model trained by the new algorithm will outperform the state-of-the-art systems following the competition’s official evaluation metrics.
Configuration
The following libraries were used in the code implementation. The compatibility was not tested on other TensorFlow versions.
- Python 3.6.4
- NumPy 1.14.3
- Scikit -learn 0.18.1
- TensorFlow (GPU version) 1.8.0
- Pandas 0.20.1
- Gensim 3.4.0
- Nltk 3.3.0
- Scipy 0.19.0
- Pyemd 0.5.1
Instruction for running the code
Installation
Download GoogleNews-vectors-negative300.bin.gz , Google’s pretrained word2vec model in to folder google_news. No other separate installation is required. Then unzip the Dataset.rar from file Dataset to the src file (Fake_News_Stance_Detection).
Reproducing the result for FNC-1 evaluation
Execute pred.py file in load mode. This entails the following actions:
- The testing dataset will be loaded class FNCData in util.py.
- Function restore_model in pred.py will be intrigued which loads pre-trained models from checkpoints which are stored in file model.
- The models are used to generate predictions separately, then ensembled for a final prediction.
- Last. The predictions are saved in prediction_test.csv file and the performance index like accuracy and FNC-1 grade are saved in Performance.csv.
Retrain the model
- To generate keywords with stance class based mutual information algorithm, open stance_mi.py and specify the training documents. The training documents should follow the FNC format where one document contains a title/body pair with stance labels and one document contains body ID and body text. Then simply execute the python file, a list of words will be displayed directly on the command window. The number of words displayed can be adjusted at the last line of the coding.
- To generate keywords with customised class based mutual information algorithm, open mutual_information.py and specify the training documents and customised topic words in method mutual_information. Then simply execute the python file, a list of words will be displayed directly on the command window. The number of words displayed can be adjusted at the last line of the coding.
- To generate keywords with PMI algorithm, open pmi.py and specify the training documents. Then in method PMI specify two lists of words. Each list towards to a semantic orientation. Then simply execute the python file, a list of words will be displayed directly on the command window. The number of words displayed can be adjusted at the last line of the coding.
After the keywords are obtained, input them into function mutual_information_title and mutual_information_body in file refuting.py. Last, specify the model type in pred.py and execute it with mode train.
For more details please refer to the project page in research gate